Will Kim Jong Un Give Up North Korea’s Nukes? History Says No
If U.S. President Donald Trump presses Kim Jong Un to give up his nuclear arsenal when they meet, he’ll be asking the North Korean leader to surrender more than a half century’s labor.
North Korea has as many as 60 nuclear weapons, an achievement spanning three generations of Kims. They’ve repeatedly chosen the bomb as the best guarantee of survival despite decades of negotiations, international sanctions and threats of war.
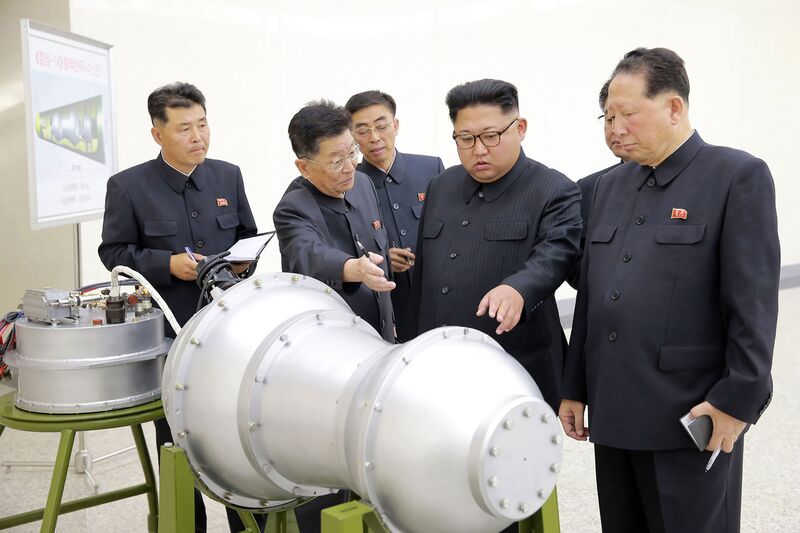

Nuclear weapons have also become central to the regime’s identity — and its propaganda efforts. North Korea’s status as a “nuclear state” is enshrined in its constitution, and Kim recently built monuments to commemorate last year’s tests of intercontinental ballistic missiles capable of reaching the U.S.
That history is why arms-control experts urge caution as Kim expresses a willingness to discuss “denuclearization” during an unprecedented summit with Trump in May or June. Giving up nuclear weapons is more than just a tactical choice: It would signal a fundamental change in how one of the world’s longest ruling dynasties maintains power.
“Without the bomb, North Korea is Albania,” said Ralph Cossa, president of the Center for Strategic and International Studies’ Pacific Forum. “No one would take it seriously. It could still threaten Seoul, but certainly not much beyond the peninsula.”
Here are some key moments in North Korea’s nuclear quest.
1950s: U.S. Nukes Arrive
The threat of nuclear war loomed over the Korean Peninsula from the conflict’s start in 1950, five years after U.S. subdued neighboring Japan with a pair of atomic blasts. While the 1953 armistice ended hostilities, U.S. President Dwight Eisenhower later deployed nuclear weapons to South Korea. Kim Il Sung, North Korea’s founder, sought a nuclear weapon from the Soviet Union.

1960s: Soviet Help
Eisenhower’s move fueled a regional scramble for nuclear technology, with the superpowers aiding less-developed states. Soviet physicists and engineers helped Kim Il Sung build the Yongbyon Nuclear Research Center in the 1960s, which would produce the fissile material for North Korea’s first bomb tests decades later.
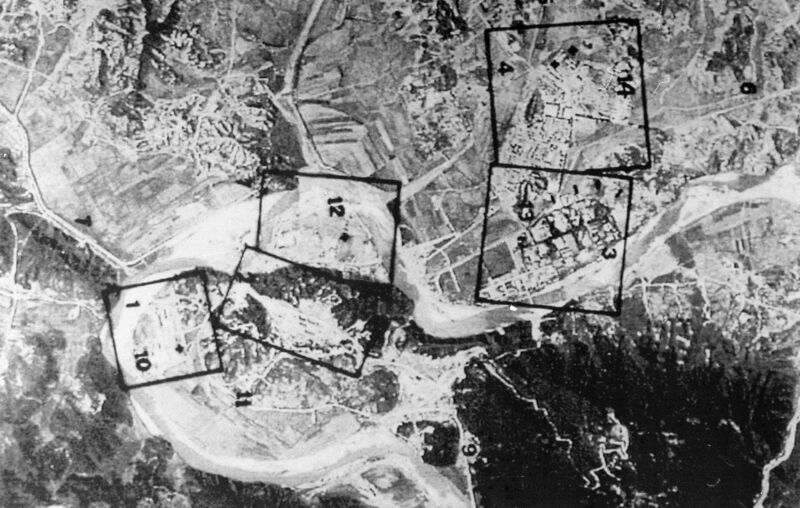

1970s: Self-Reliance
A confluence of events — severe drought, surging oil prices and U.S.-Soviet non-proliferation talks — encouraged Kim Il Sung to accelerate domestic reactor development in the 1970s. The power plants fit with his guiding philosophy of Juche — often translated as “self-reliance” — as sources of both electricity and waste that could be processed into weapons-grade plutonium.

1980s: Peace Hopes
North Korea raised hopes that it may abandon nuclear weapons after the Soviets convinced it to sign the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty in 1985. Those expectations soon faded after U.S. intelligence analysts viewing satellite photos of the expanded Yongbyon complex concluded that Kim Il Sung was in the early stages of building a bomb.
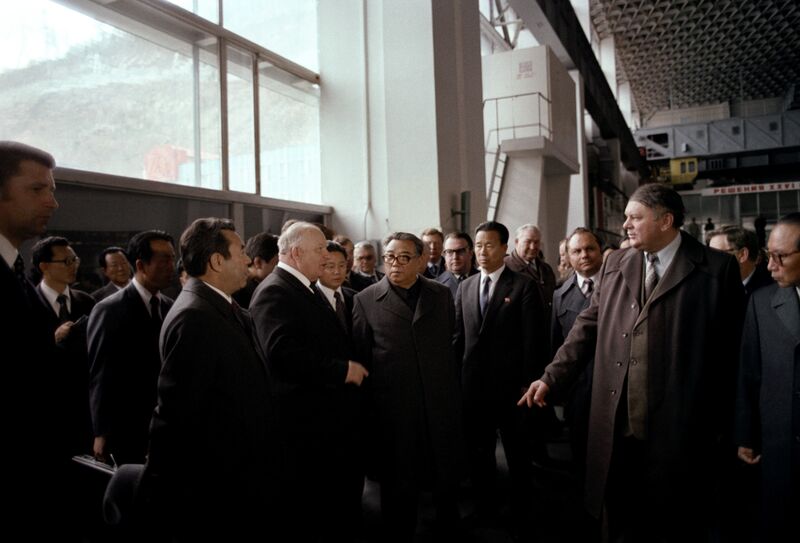

1990s: U.S. Nukes Leave
U.S. President George H.W. Bush recalled nuclear weapons from South Korea and other sites as the Cold War ended, creating new space for talks. Bill Clinton’s administration signed an agreement with North Korea in 1994 that would see Pyongyang freeze work on its nuclear weapons program in return for reactors that couldn’t be used for proliferation. The deal broke down after the regime launched a missile over Japan in 1998 (North Korea says it carried a satellite).
2000s: Axis of Evil
President George W. Bush placed North Korea alongside Iran and Iraq in his “Axis of Evil.” Kim Jong Il — the founder’s son — eventually agreed to abandon “all nuclear weapons and existing nuclear programs.” But talks on implementing the deal broke down and Pyongyang resumed weapons tests, detonating its first atomic bomb in 2006. Kim Jong Il walked away from talks for good in 2009 and tested his second bomb soon after.
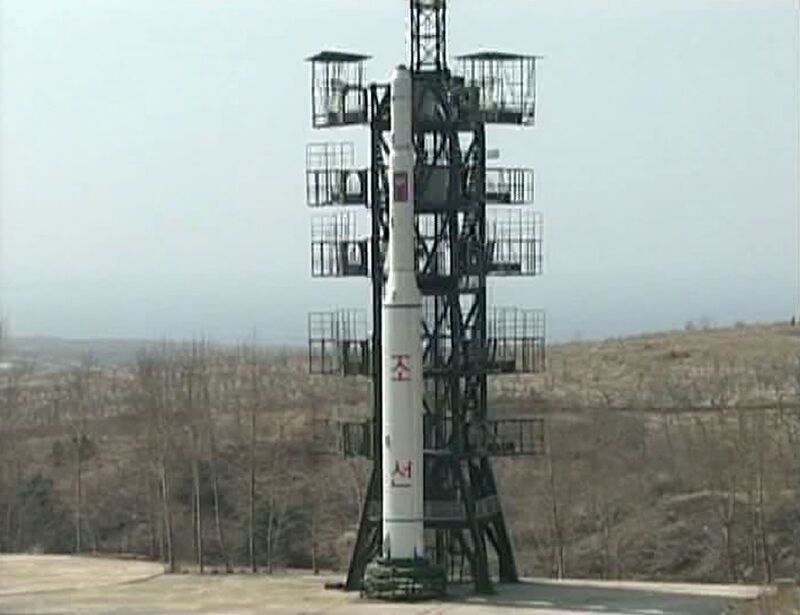

2010s: The Dictator’s Fall
President Barack Obama’s moves to help to oust Libyan leader Muammar Qaddafi, who had surrendered his nuclear weapons, reaffirmed North Korea’s resolve to accelerate its program. Kim Jong Un, who took power two months after Qaddafi’s death, stepped up bomb and missile testing, and declared in November he could strike the U.S. with a nuclear weapon. Trump, meanwhile, tightened sanctions and threatened “fire and fury” to stop him.
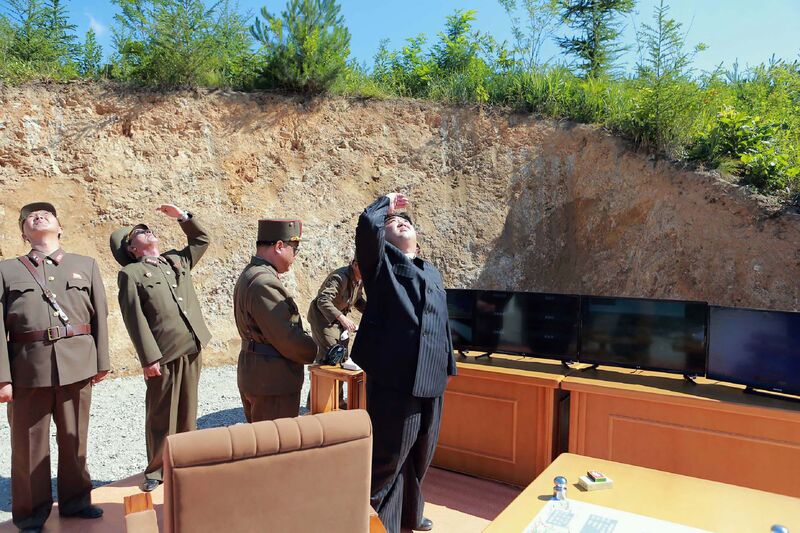

Now: Unprecedented Meeting
Kim opened the door to talks with South Korea in an annual New Year’s Day speech, and a few months later Trump made a surprise decision to meet him — a request U.S. presidents had denied for decades. Many analysts are skeptical that Trump can convince Kim to finally give up his nuclear weapons and forge a new identity.
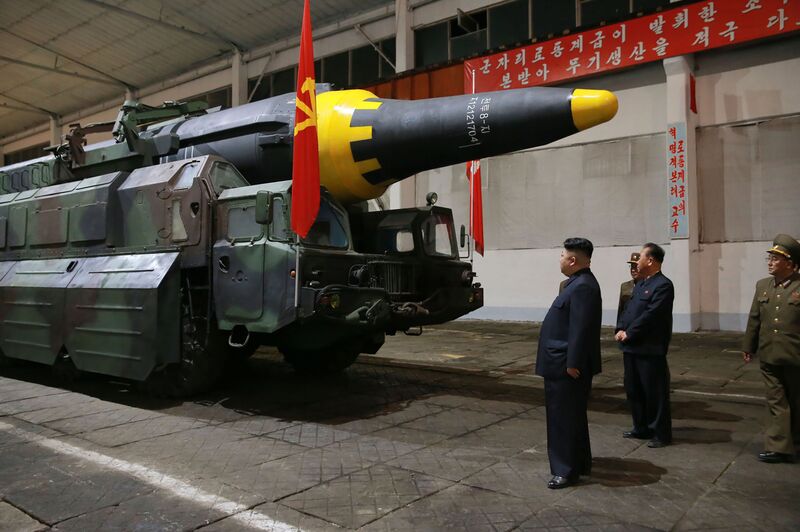

“They don’t want to see all their impressive achievements go down the drain,” said Andrei Lankov, a historian at Kookmin University in Seoul who once studied in Pyongyang. “If they surrender nuclear weapons, they will sign their own death warrant.”
Source: Bloomberg
READ ALSO: 45 police officer promoted for arresting kidnap kingpin